
Overview of the Development of the Cryptocurrency Market
1.1 Current Status and Trends of the Cryptocurrency Market
2024 was a milestone year for the cryptocurrency market. The price of Bitcoin surpassed $100,000 for the first time, and with multiple favorable macroeconomic factors converging, the cryptocurrency market experienced its strongest growth cycle since 2017. Against this backdrop, the cryptocurrency market in 2025 is poised to embrace new opportunities for development.
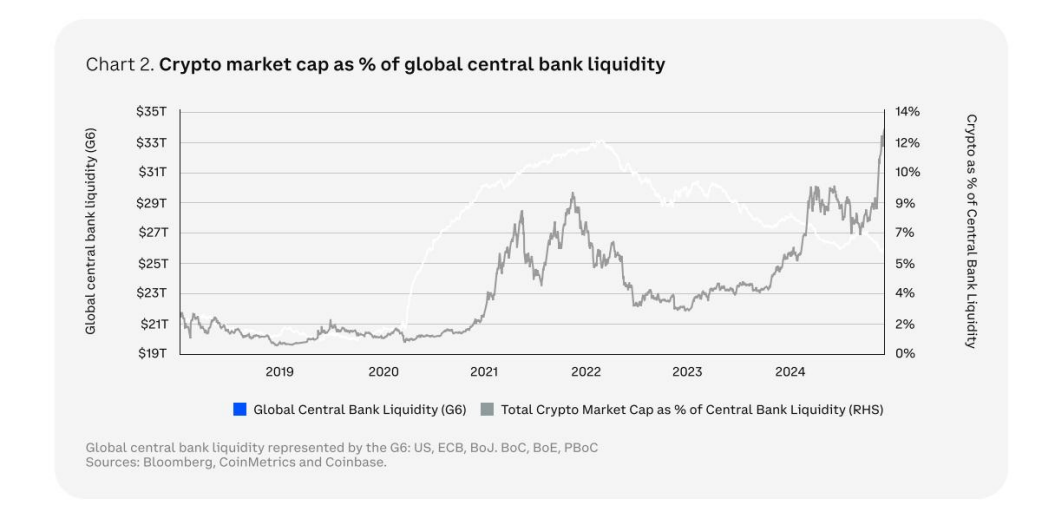
The main drivers will include: the recovery of the global economy and the reduction of inflationary pressures. The Federal Reserve's interest rate cut cycle has created a more favorable macroeconomic environment for high-risk assets. The institutional adoption of Bitcoin and other digital assets has increased rapidly with the implementation of fair value accounting rules. The evolution of blockchain technology, such as the maturity of Layer 2 and Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP), will enhance user experience and expand the application scenarios of blockchain. These changes indicate that the cryptocurrency market in 2025 will not only be driven by price but will also enter a new phase centered on technological breakthroughs and the perfection of the ecosystem.
1)Global Macroeconomic Environment of the Cryptocurrency Market
The global macroeconomic environment will have a profound impact on the cryptocurrency market. In 2025, the interest rate cut cycle, the decline of inflation, and the demand from emerging markets will become the main drivers for the continuous growth of cryptocurrency assets.
- Interest Rate Cycle and Cryptocurrency Assets
- Federal Reserve's Interest Rate Cut Background: At the end of 2024, the Federal Reserve officially entered an interest rate cut cycle. Due to the high-interest rate policies in 2022-2023, the global economy faced certain growth pressures, and the interest rate cuts injected new liquidity into the capital market. Against this background, cryptocurrency assets, as a highly elastic asset class, became an important target for capital flows.
- Dual Nature of Cryptocurrency Assets as "Risk Assets" and "Safe-Haven Assets": Risk asset nature—The interest rate cut environment reduced the expected returns of traditional financial assets, driving capital into high-growth, high-volatility markets. Bitcoin, due to its historical performance, is seen as a risk asset with great potential. Safe-haven asset nature—At the same time, Bitcoin, with its limited supply and non-governmental intervention characteristics, is gradually being regarded as "digital gold" by institutions and countries, providing a safe-haven function against inflation and economic uncertainty.
- Correlation of Cryptocurrency Assets with Other Assets: Research shows that the correlation of Bitcoin with traditional assets such as gold and the S&P 500 changes periodically. After 2024, the correlation of Bitcoin with the stock market weakened, while its correlation with gold slightly increased, indicating that investors are gradually incorporating Bitcoin into their safe-haven asset allocations.
- Inflationary Pressures and Demand for Reserve Assets
- Global Inflation Decline: Although global inflationary pressures eased gradually in 2024, geopolitical risks and supply chain issues could still lead to local economic fluctuations. Against this backdrop, enterprises and investors are more inclined to use Bitcoin as a reserve asset to hedge against potential uncertainties.
- Bitcoin Adoption in Latin American and African Markets: For example, in high-inflation countries such as Argentina and Zimbabwe, the demand for Bitcoin and stablecoins by residents and enterprises has increased significantly. Data shows that the volume of cryptocurrency transactions in these regions grew by more than 200% year-on-year in 2024.
- Emerging Markets and Digital Currencies
- Role of Stablecoins: The role of stablecoins in payments and savings in emerging markets is becoming increasingly important. For example, USDT dominates cross-border payments in Southeast Asia, solving the problem of low efficiency in the banking systems of many countries.
- Development of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): In 2025, the central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) of several countries will enter the testing or application phase. For example, China's digital yuan (e-CNY) continues to expand its international influence, driving other countries to accelerate research and deployment of similar projects.
2)Evolution of Blockchain Technology and Ecosystem
Blockchain technology is one of the core drivers of the development of the cryptocurrency market. In 2025, the blockchain industry will enter a new phase that is more efficient and widespread. The evolution of technology will expand application scenarios and empower the continuous growth of the entire cryptocurrency market.
- The Outburst of Layer 2 Technology
- Definition and advantages of Layer 2: Layer 2 is an important innovation in blockchain technology, aimed at solving the limitations of Layer 1 public chains (such as Ethereum) in terms of scalability, transaction speed, and cost. In 2025, with the maturity of technologies such as Optimistic Rollups and ZK Rollups, Layer 2 will not only become an important pillar of the Ethereum ecosystem but also provide expansion capabilities for other public chains.
- Main projects and developments: Arbitrum and Optimism: In 2025, it is expected that more than 70% of Ethereum's transaction volume will migrate to the Layer 2 network. Arbitrum's expansion solution will continue to expand ecological applications, while Optimism will support cross-chain interoperability of more chains through its "Superchain" plan. The rise of ZK Rollups: ZK Rollup projects such as ZK Sync and StarkNet, with their lower latency and strong privacy, are becoming the preferred solution for emerging decentralized finance (DeFi) applications.
- Driving the ecosystem: The development of Layer 2 will reduce user costs, enhance user experience, and inject new vitality into areas such as decentralized finance (DeFi), NFTs, and blockchain games. At the same time, Layer 2 will also attract users of traditional Web2 applications to migrate to the blockchain ecosystem.
- Breakthrough and Application of Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP)
- Overview of ZKP Technology: Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP) is a cryptographic method that allows one party to prove the truth of a statement to another party without revealing any additional information. In the blockchain field, ZKP is considered a key technology for future privacy protection and scalability enhancement.
- Applications of ZKP in 2025: Private transactions - ZKP can be used to achieve completely private cryptocurrency transactions, such as upgraded versions of Monero and Zcash. Identity verification - KYC (Know Your Customer) verification can be completed without revealing personal information, resolving the contradiction between privacy and compliance. Cross-chain interoperability - Using ZKP to solve trust issues in cross-chain communication, providing more efficient solutions for multi-chain ecosystems.
- Maturity of Multi-Chain and Cross-Chain Ecosystems
- Rise of Multi-Chain Ecosystems: Over the past few years, the limitations of single public chains have led to the rise of multi-chain ecosystems. In 2025, the widespread adoption of cross-chain protocols will completely break the island effect between blockchains. Polkadot and Cosmos: As representatives of multi-chain ecosystems, Polkadot's parallel chain auctions and Cosmos's IBC (Inter-Blockchain Communication protocol) will continue to drive ecological expansion. Uniswap's UniChain: The dedicated Layer 3 network launched by Uniswap will become an important case for performance enhancement of decentralized exchanges (DEXs) within the Ethereum ecosystem.
- Innovation of Cross-Chain Protocols: Bridge protocols, such as Wormhole and Axelar, will further enhance the cross-chain interoperability of assets and data in 2025. Security issues: Multiple cross-chain bridge attack incidents in 2024 exposed security risks, and technological innovations in 2025 will focus more on the security and trustless design of cross-chain transactions.
- Impact on the Industry: The development of multi-chain and cross-chain ecosystems will create greater development space for decentralized applications (DApps) and provide more choices for users, promoting the diversity of the cryptocurrency industry.
In 2025, the evolution of blockchain technology will be centered around Layer 2, ZKP, multi-chain ecosystems, and decentralized storage, driving the industry into a stage of deepened application. At the same time, the involvement of AI and the technological evolution of NFTs will inject new vitality into the blockchain ecosystem. In the future, technological breakthroughs will not only be reflected in performance but also in the diversification of user experience and application scenarios.
1.2 Cryptocurrency Exchange Market
In the entire field of cryptocurrency, exchanges play the most critical role in circulation, trading, and value exchange. Therefore, as one of the most important links in the entire cryptocurrency market ecosystem, exchange platforms hold an irreplaceable position. The most important function of an exchange is to convey the value of a project's cryptocurrency to all investors, tightly connecting them. As cryptocurrency has developed, the number of digital asset exchanges has also been increasing.
The functions and characteristics of cryptocurrency exchanges are as follows:
- Asset trading: Offering a variety of digital asset trading pairs to meet users' diverse investment needs.
- Security: Implementing multiple security measures to protect users' assets, such as cold and hot wallet storage, two-factor authentication, etc.
- Liquidity: Providing a highly liquid trading environment to ensure that users can complete transactions quickly and smoothly.
- User experience: Offering an intuitive and user-friendly trading interface and stable, fast transaction execution to enhance user experience.
1)Exchange Trading Models
Currently, exchange trading models can be broadly categorized as follows:
- Limit order model: In limit order trading, users set a specific price and quantity, and the system searches for matching orders in the market based on the set price and quantity. If there are matching orders in the market, the trade will be executed immediately; otherwise, the order will be suspended until a matching order appears.
- Market order model: Market order trading is not restricted to a specific price but is based on the current market price. In market buy orders, users set a total amount, and the system matches orders starting from the lowest sell price until the total amount is traded. In market sell orders, users set the total number of coins to sell, and the system matches orders starting from the highest buy price until all coins are traded.
- Crypto-to-crypto model: Crypto-to-crypto trading involves using one virtual digital asset as the pricing unit and another virtual digital asset for the transaction. The trading rules follow a price-priority and time-priority matching sequence.
- C2C model: C2C trading involves both parties posting buy or sell information on a C2C trading platform and completing the transaction offline. The platform acts as an intermediary and collects a certain percentage of fees from each successful transaction.
- OTC model: Over-the-counter (OTC) trading refers to the buying and selling of digital currencies outside the exchange. Merchants can post buy/sell ads on the platform, and both parties complete the transaction through offline transfers. After the transaction is completed, the platform transfers the frozen digital currency to the buyer.
- Reward model: The reward model involves the exchange platform returning a certain percentage of transaction fees to users in the form of platform tokens. Users gradually unlock these platform tokens through trading on the platform until the full amount is returned.
- Futures/contract model: A futures contract is an agreement where the buyer agrees to receive a specific asset at a set price after a designated time, and the seller agrees to deliver the asset at that price after the same time. The price agreed upon for future transactions is called the futures price, and the designated date for the transaction is called the settlement or delivery date.
- Perpetual contract model: A perpetual contract is a contract that does not have a delivery date, aiming to replicate the conditions of the spot market and allow high-leverage trading. Compared to traditional futures contracts, perpetual contracts offer greater flexibility and risk, supporting features such as long and short。
2)Market Data Analysis
In the fourth quarter of 2024, the total market value of the cryptocurrency market increased by 45.7% (i.e., $1.07 trillion), closing at $3.40 trillion. Although the market lost some momentum in the third quarter, it rebounded in the middle of the fourth quarter after a brief period of bottom oscillation, especially after Donald Trump won the U.S. presidential election.
In 2024, the total market value of the cryptocurrency market nearly doubled, increasing by 97.7%. Its market value reached a historical high of $3.91 trillion in mid-December, before falling back to $3.40 trillion. Meanwhile, the average trading volume in the fourth quarter of 2024 was $200.7 billion, a 128.2% increase from the third quarter's $88 billion.
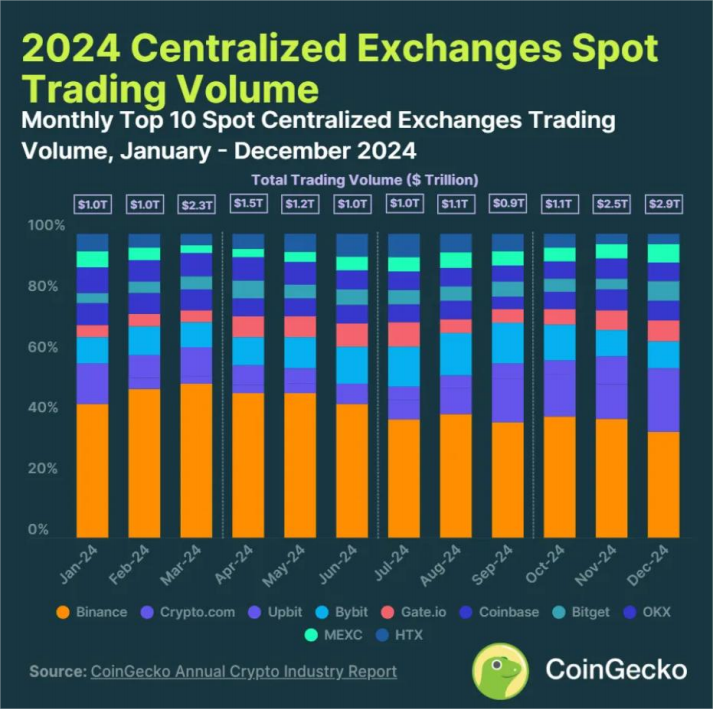
Currently, the 24-hour trading volume of the top 10 global exchanges accounts for 90% of the total trading volume. In the fourth quarter of 2024, the spot trading volume of the top 10 centralized exchanges (CEX) reached $6.5 trillion, a quarter-on-quarter increase of +111.7%. This was the first time the quarterly trading volume broke through the $6 trillion mark. The total trading volume of the top 10 CEX in 2024 was $17.4 trillion, compared to $7.2 trillion in 2023.
1.3 Market Pain Points Analysis
As a critical link and bearer of value circulation in the cryptocurrency market, the exchange market has developed rapidly but has also accumulated many problems that urgently need to be solved.
For example, the black swan event of the cryptocurrency exchange FTX caused a strong shock in the global cryptocurrency community. FTX fell from the world's second-largest exchange to bankruptcy in just 10 days, with its $32 billion valuation dropping to zero. FTX's unscrupulous use of customer funds also caused a significant trust crisis in centralized exchanges within the cryptocurrency community.
At present, centralized exchanges (CEX) in the market mainly face the following problems:
- Asset Security Risk: Assets are fully custodied by the platform
The account created by the user on the exchange is similar to the bank card account provided by the bank to the user. The exchange stores the assets that users deposit into the platform in its own digital asset wallet. If the exchange's wallet is attacked or the platform itself acts maliciously, the user's assets will be severely threatened.
- Asset Control Restrictions: Users cannot freely control their assets
Users only have the password to their exchange account and cannot actually control their assets. If a user wants to withdraw assets from the exchange, they need to click to withdraw to their personal wallet address in the exchange account. However, exchanges often set rules to limit user withdrawals, including restricting withdrawal amounts, withdrawal times, and setting withdrawal fees, thereby affecting users' free control over their assets.
- Non-transparent Trade Settlement: The settlement process is completed by the platform and cannot be traced on the blockchain
The order placement, order matching, and settlement processes that users conduct on the exchange are all assisted by the exchange's servers and are conducted off-chain. Users have no way of seeing the real situation. Therefore, exchanges can easily create fake trades and manipulate prices.
In addition, decentralized exchanges (DEX) also face some problems, such as:
- Low Trading Speed
Trades on DEXs are usually much slower than on CEXs. This is because every transaction order and status change on a DEX is recorded on the blockchain network and requires miner validation. When quick reactions to changing market conditions are needed, DEXs are not suitable as fast trading platforms. In contrast, CEXs, which do not record transaction data on-chain, can match orders almost instantly, resulting in extremely fast trade execution. For example, Binance's servers can process 1.4 million orders per second.
- High Trading Costs
Transaction fees on DEXs can fluctuate and may be much higher than on CEXs. When on-chain transactions are congested, gas fees can soar, leading to higher trading costs on DEXs. In contrast, CEXs, which do not conduct on-chain transactions, have fixed transaction fees set by the exchange itself.
In addition, both CEXs and DEXs face the problem of market concentration. The market is overly concentrated in a few exchanges. Currently, the top few exchanges control nearly 90% of the cryptocurrency market's trading volume. The most notable development in recent years is Binance's absolute leading position—its share of global trading volume has almost doubled to 64%. This phenomenon poses the potential danger of concentrated liquidity, which can lead to a single point of failure and cause a large amount of liquidity to disappear, as seen in the FTX collapse.
To change the current market situation, new forces are needed. The emergence of CriptoAuge represents the rise of a new force, aimed at dispersing the risks associated with overly concentrated market liquidity. At the same time, through technological and functional innovations, CriptoAuge aims to address the pain points of both CEXs and DEXs.
1.4 The Genesis of CriptoAuge
In response to the transformations brought about by digitalization, assetization, and new finance, the existing crypto-financial infrastructure and services are no longer sufficient. A set of solutions and service schemes that are compatible from concept to design to implementation is required. Therefore, the CriptoAuge Ecological Development Fund, with CriptoAuge at its core, has created a comprehensive solution and a multi-currency trading service ecosystem that is more suitable for the current market situation.
Since the birth of Bitcoin, digital assets based on blockchain technology have flourished. Today, the variety and influence of digital assets are growing daily. The formation of fair prices for digital assets, the exchange transactions between different digital assets, as well as related customer services, regulatory compliance, and even the trading of digital asset derivatives are all basic needs. These needs are currently supported by a variety of digital asset trading platforms. In the short development period of digital assets, these trading platforms have played a significant role, but they are also accompanied by serious problems. These problems are less a fault of the trading platforms themselves than a sign that traditional models of trading platforms can no longer meet the demands of the new digital asset era.
The emergence of digital assets based on blockchain technology has made full transparency and self-certification of assets and transactions possible. This will drive the transformation of future platforms and regulatory governance structures. We believe that the direction of this transformation is the evolution of platforms towards communities and the alignment of regulation with technology. Digital asset trading platforms themselves have the ability and responsibility to lead this change. Therefore, CriptoAuge has made the construction of a secure, stable, fair, transparent, and widely traded exchange its core value pursuit, aiming to create a new one-stop trading ecosystem for global users.
- Based on user interests, adopt a low-fee strategy to capture market share.
CriptoAuge adopts an innovative model, offering ultra-low transaction fees to global professional users, which are more competitive than those of exchanges like Huobi, OKEx, and Binance. Coupled with the exchange's strong information research capabilities, this strategy maximizes the benefits of investors.
- Utilizing World-Class Technical Standards
CriptoAuge boasts a world-class trading technology architecture, employing a multi-layered, multi-cluster system structure and a multi-variety trading approach to provide a more secure, stable, and efficient trading experience. It includes underlying foundational capabilities, distributed core protocols, gateways, and client-side distributed capabilities. These ensure data consistency, network stability, reliable consensus, and service availability on a decentralized basis. Moreover, these foundational capabilities are exposed through a comprehensive OpenAPI, allowing seamless integration with other financial components and services, thereby better supporting the construction of DeFi scenarios.
- Seamless Cross-Border Capital Flow
CriptoAuge establishes a new monetary and financial system, providing a convenient channel for capital flow. Value transfer through digital currency not only breaks through regional regulatory restrictions but also bypasses expensive intermediary institutions, effectively reducing the cost of cross-border capital circulation.
- Solid Trust Foundation
In digital scenarios, many risk control measures face the risk of failure or inapplicability, threatening the core trust foundation of transactions. CriptoAuge leverages blockchain technology, relying on data and cryptography, to build a more robust trust from the ground up under the premise of minimal trust assumptions, thereby laying a more solid foundation for transactions.
 CriptoAuge
CriptoAuge